A 19 year-old female patient with lumbago and periumbilical pain went to Medic Center for ultrasound examination for 10 days.
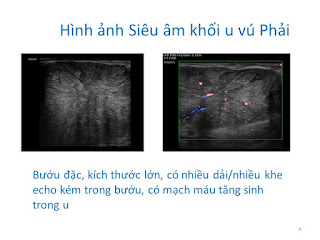
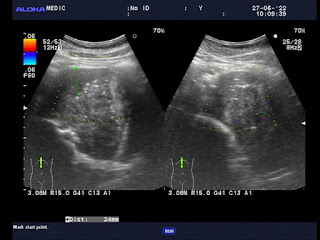
Abdomen ultrasound detects a calcified mass, colorless signal, close by the vertebral column on left side which is thought a TB abscess or a retroperitoneal tumor. On vertebral X-ray films there are erosions of the vertebral bodies T 11 and T 12.
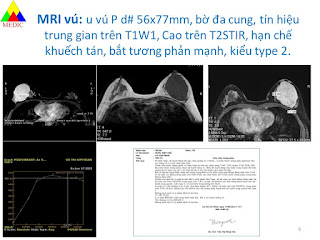
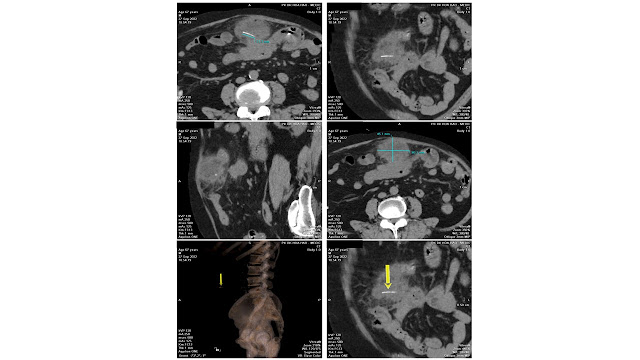
MSCT confirms a tissue density mass, well limited, with calcifications inside, # 11x17x7 cm, medium contrast captured. From under the diaphragm the mass compresses left kidney and soft tissues around and erodes vertebral bodies T11, T 12. It may be a retroperitoneal neurogenic tumor.
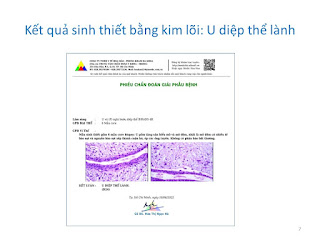
Surgery was done after ten days of diagnosing made and post-op result is a retroperitoneal ganglioneuroma.
Now the patient remains well and no need any other treatment.
REFERENCES
1. Sawaryn T. Ganglioneuroma of the mediastinum. Pol Tyg Lek 1959;14:867–70. 1959/05/11.
2. Hayat J, Ahmed R, Alizai S, et al. Giant ganglioneuroma of the posterior mediastinum. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 2011;13:344–5. https://doi.org/10. 1510/icvts.2011.267393. 2011/06/23.
3. Kiflu W, Negussie T. Ganglioneuroma of the Neck: a case report. Ethiop Med J2017;55:69–71. 2017/11/18. 4. Geoerger B, Hero B, Harms D, et al. Metabolic activity and clinical features of primary ganglioneuromas. Cancer 2001;91:1905–13. https://doi.org/10.1002/ 1097-0142(20010515)91:10<1905::aid-cncr1213>3.0.co;2- 4. 2001/05/11.
5. Kizildag B, Alar T, Karatag O, et al. A case of posterior mediastinal ganglioneuroma: the importance of preoperative multiplanar radiological imaging.Balkan Med J 2013;30:126–8. https://doi.org/10.5152/balkanmedj.2012.099. 2013/03/01.
6. Mylonas KS, Schizas D, Economopoulos KP. Adrenal ganglioneuroma: what you need to know. World J Clin Cases 2017;5:373–7. https://doi.org/10.12998/wjcc. v5.i10.373. 2017/11/01.
7 . Yorita K, Yonei A, Ayabe T, et al. Posterior mediastinal ganglioneuroma with peripheral replacement by white and brown adipocytes resulting in diagnostic fallacy from a false-positive 18F-2-fluoro-2-deoxyglucose- positron emission tomography finding: a case report. J Med Case Rep 2014;8:345. https://doi.org/ 10.1186/1752-1947-8-345. 2014/10/17.
8. Sucandy I, Akmal YM, Sheldon DG. Ganglioneuroma of the adrenal gland and retroperitoneum: a case report. N Am J Med Sci 2011;3:336–8. https://doi.org/10. 4297/najms.2011.3336. 2012/04/28.


























.jpg)