Young female patient came to clinic with chief complaint intermittent claudication for months. On
clinical exam salient abnormality is mild hypertension 150/80mmHg, legs skin has few telangiectasia.
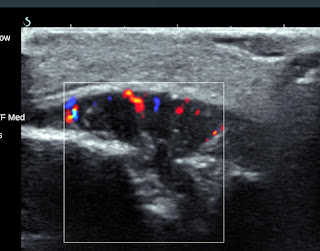
Doppler ultrasound in legs shown normal venous system and monophasic waveform throughout
FEMORAL arteries-> POSTERIOR TIBIAL arteries. So, the stenosis must from above and compensate with collaterals since high diastolic velocity tell us (PIC 1).
On abdominal ultrasound exam, monophasic waveform in both ILIAC arteries and aortic dilation at
bifurcation, above that, no obstruction detected (PIC 2).
Noticed AORTA quite small from below SUPERIOR MESSENTERY artery, transitional point is subtle d=7.3->6.9mm (PIC 3,4). Renal arteries aliasing in both side, high PVS R=189cm/s L=193cm/s at α=60 degree, RIR=6.3, normal interlobular waveform AT<0,07s, they could suggest the stenosis range 50-69% (PIC 5).
CTA confirmed the stenosis and large collateral pathway in pelvic.(PIC6) Most narrow aorta diameter d=6mm, Aorta diameter below stenosis=17.4mm. Right renal artery d=4.8mm, Left renal artery=3.1mm As this occurred in young patient it could possibly Mid-aortic Syndrome or type II TAKAYASU disease.
The two disease differentiated by histopathology of inflammatory change, which is present in Takayasu arteritis but not in MSD. Lacking of signature US sign “macaroni” or ”halo sign”, CTA no sign of lumen thickness, Takayasu is less favored in this case.
Patient currently treated with hypertension controller since the legs are perfused by the large collateral.
Mid-aortic dysplasia syndrome (MDS), is a rare disease characterized by constriction of abdominal aorta and its branches, therefore, is also known as abdominal aortic coarctation. Patients usually die due to progressive severe hypertension before age of 35–40 if left untreated. Etiology is unknown but embryological theory, failure in fusion of the paired dorsal aorta during the fourth week of gestation
may cause MDS. Acquired conditions such as infection, obliterative panarteritis, neurofibromatosis,
retroperitoneal fibrosis, fibromuscular dysplasia, mucopolysaccharidosis and Takayasu’s arteritis have been incriminated in MAS. Approximately 60% of cases, no etiology can be found. The renal arteries are involved in about 90% of the cases, the coeliac axis and superior mesenteric artery in 35–50%, while the inferior mesenteric artery is almost never affected. A common histopathological finding in idiopathic
MDS is fibroplasia of the intima and internal elastic lamina distortions with a lack of inflammatory
changes that characteristically distinguish it from Takayasu’s arteritis. [1]
1. Saha K, Saha D, Ranjit P, Sarkar S, Mondal RRS, Thiyagrajan G. Mid aortic dysplastic syndrome as a rare cause of hypertension in young. International Journal of Case Reports and Images 2013;4(10):563–566.