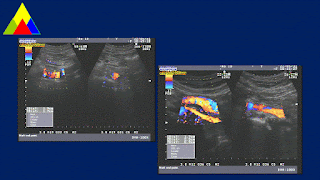
A 56 year-old female patient suffered from epigastric pain for one month with out fever. WBC 18,880/L , hCRP 129.5mg/L.
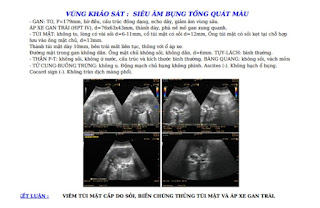
Ultrasound of abdomen revealed an abscess of liver that came from a cholecystitis due to stone. Gall bladder wall thickening was perforated that connected to the abscess. And there were stones in CBD and cystic duct.
MRI was done before a surgical treatment.
Endoscopic surgery at first but it did to change to open surgery to take away the hepatic abscess, that was in GB bed. Inflammed GB adhered to liver, mesentery and duodenum that has been dissected difficultly.
Surgeons performed partial cholecystectomy, and Kehr drainage after removing stones in CBD and in cystic duct.
DISCUSSION and CONCLUSION:Hepatic abscess due to perforated cholecystitis with biliary stone is still a rare entity. Ultrasound could detect successfully cholecystitis due to biliary stone [84-97 % sensitive, and 95-97% specific] that seems to be higher than CT or MRI does.