Total Pageviews
Tuesday 8 September 2020
CASE 596: SEVERE STENOSIS of ILIAC ARTERY, Dr PHAN THANH HẢI, Dr NGUYỄN NGHIỆP VĂN, Dr VÕ NGUYỄN THÀNH NHÂN, Dr VÕ HIẾU THÀNH, Dr HỒ KHÁNH ĐỨC, MEDIC MEDICAL CENTER, HCMC, VIETNAM.
Sunday 6 September 2020
CASE 595: HCC WITH NEGATIVE WAKO TEST, Dr PHAN THANH HẢI, MEDIC MEDICAL CENTER,HCMC,VIETNAM
In check-up, ultrasound detected one round mass # 3cm look like a cyst.
WAKO tests= AFP=5.7, L3= 0.5, DCP=16.
MSCT with CE detected non tumor.
MR image shows a lesion in hepatic segment V; with the size 24mm, well-defined. The lesion demonstrates high signal intensity on T2WI and low signal intensity on T1WI.
The lesion had restricted on Diffusion Dynamic MRI: On arterial phase image demonstrates unequivocal arterial enhancement relative to the surrounding liver; On the portal venous phase has decreased in enhancement relative to the surrounding liver (washout); On the delay phase has decreased in enhancement relative to the surrounding liver and enhance capsule is found which helps further solidify the imaging diagnosis of HCC.
-This patient has negative Wako test. Volk et al (2007) and Hann et al (2013) demonstrate of Wako test with sensitivity (83%) and specificity (>90%) for detecting HCC.
Operation removed the liver tumor.
Saturday 29 August 2020
CASE 594: LUNG TUMOR ON PATIENT WITH CORONARY STENTS, Dr PHAN THANH HẢI, Dr DƯƠNG PHI SƠN, MEDIC MEDICAL CENTER,HCMC VIETNAM
CASE 593: HYPERTHYROIDISM and DIARRHEA, Dr PHAN THANH HẢI, Dr TRƯƠNG CÔNG THÀNH, MEDIC MEDICAL CENTER, HCMC, VIETNAM
Wednesday 22 July 2020
CASE 592: FOCAL NODULAR HYPERPLASIA of LIVER (FNH), Dr PHAN THANH HẢI, Dr TRƯƠNG ĐÌNH KHẢI , Dr NGUYỄN SÀO TRUNG, Dr HỒ CHÍ TRUNG, Dr NGUYỄN THÀNH ĐĂNG, MEDIC MEDICAL CENTER, HCMC, VIETNAM
Tuesday 21 July 2020
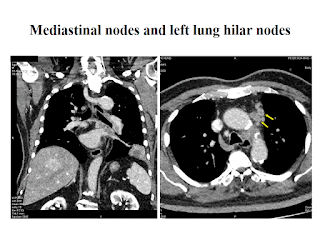
CASE 591: RIGHT LUNG MULTIPLE NODULES, Dr PHAN THANH HẢI, Dr LÊ THANH LIÊM, MEDIC MEDICAL CENTER, HCMC, VIETNAM
No lymph node at neck, axilla, inguinal regions and inside abdomen.
Monday 20 July 2020
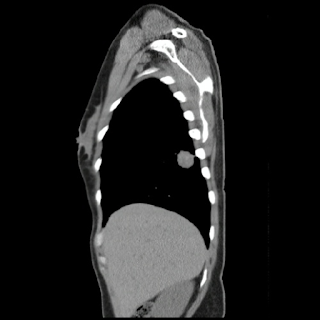
CASE 590: INFECTIOUS THORACIC AORTIC ANEURYSM, Dr PHAN THANH HẢI, Dr CHÂU NGỌC MINH PHƯƠNG, MEDIC MEDICAL CENTER, HCMC, VIETNAM.
He was given oral antibiotics (Levofloxacin) and anti-inflammation for 7 days.