Man 52 yo with HBV chronic hepatitis , follow up every 6 months and negative AFP, HBV -DNA . But
ultrasound detected a big tumor # 6 cm in diameter in left lobe of liver.
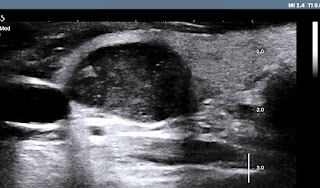
US 1: transverse scanning of this tumor
is well bordered, hypoechoic pattern.
US 2: longitudinal
scanning at tumor site.
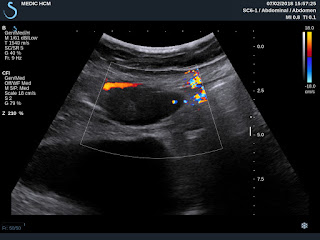
US 3: color Doppler= vascular supply to tumor is from
left liver.
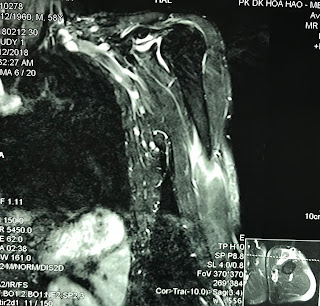
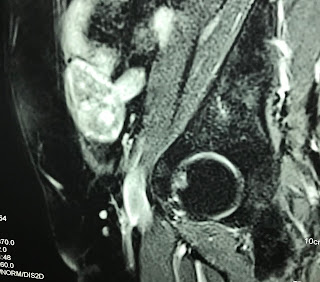
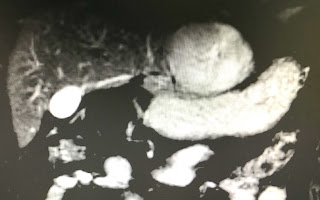
MRI with Primovist uptaked and
washed out as a HCC in liver ( MRI 1, 2, 3, 4).
Blood test Wako= only DCP raised =91 UI.
Summary: in case of HBV chronic hepatitis,, ultrasound detected a big tumor in liver,
Wako test only raised DCP.
OPERATION PER OP VIEW BY ENDOSCOPY THE TUMOR AT LEFT LOBE of LIVER ANTERIOR AND POSTERIOR and MACRO SPECIMEN of TUMOR.
MICROSCOPIC IS WELL DIFFERENTIATED HCC.
DISCUSSION: WHY IN THIS CASE WAKO TEST IS NOT SUITABLE ? WHICH VALOUR of WAKO TEST COULD BE PPV FOR HCC ?
Wako test post op 4 days after operation = AFP:1.3 ng/mL; L3: 0.5%; DCP: 55 mAU/mL.
This 52 yo male patient with chronic HBV but AFP is lower than cut of value screening and no ultrasound screening before operation. Wako test is only DCP rising to 92 mAU/mL. Reference ( publication April 12,2016 http:// doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0153227 : Diagnostic evaluation of DCP versus AFP for Hepatitis Bvirus related HCC in China):
1- 30-40% HCC in CLD with AFP normal serum level.
2- non HCC patients have 15-58% AFP rise over cutt of value 20ng/mL.
3- in CLD having cirrhosis AFP rises 11-47% but non HCC.
4- DCP rises level that correlated with size tumor and advanced progress.
5 - DCP drops very fast after surgery, and rises early in recurrent HCC.
Conclusion : AFP only not sensitive for screening HCC. So DCP in Wako test is the choice for routine screening HCC and monitoring after treatment.
BLOOD TEST WAKO AGAIN RESULT IS AFP: 1,5; L3 : 0,5; DCP DROP TO 38mUI/mL
CONCLUSION 2:
DCP IS VERY SENSITIVE FOR DETECTION of HCC AND FOLLOW UP POST OP.